Schedule a Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
General Considerations
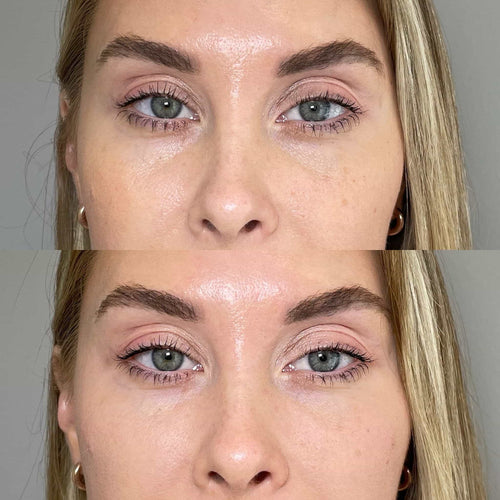
Botox, a popular cosmetic treatment for facial wrinkles and fine lines, can be administered while on certain medications, but it’s crucial to understand the potential interactions and general considerations.
**Medication Interactions**: Certain medications can affect the way Botox works, reduce its effectiveness, or increase the risk of side effects. These medications include:
- Anticoagulants (blood thinners): Medications like Warfarin (Coumadin) and aspirin can increase the risk of bleeding complications when combined with Botox.
- Antidepressants**: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as fluoxetine (Prozac) and sertraline (Zoloft), may interact with Botox, leading to an increased risk of side effects like headaches and muscle weakness.
- Beta blockers: Medications used to treat high blood pressure, glaucoma, or heart conditions can mask the symptoms of a botulism-like illness caused by Botox, making it more difficult to diagnose if an adverse reaction occurs.
- Neuromuscular blockers: Muscle relaxants like succinylcholine and rocuronium can increase the risk of respiratory complications when combined with Botox.
- Pain medications**: Certain pain medications, such as opioids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may interact with Botox, leading to increased side effects or reduced effectiveness.
- SSRI antidepressants that inhibit the enzyme CYP2D6: Medications like fluoxetine and sertraline may reduce the efficacy of Botox by inhibiting its metabolism.
**General Considerations**: When considering whether to undergo Botox treatment while on medication, it’s essential to take into account your individual medical history and the potential risks and benefits. Some general considerations include:
Informing Your Doctor: Be open and transparent about all medications you are taking, including prescription and over-the-counter substances.
Medication Classifications: Certain medication classes, such as anticoagulants and antidepressants, may be more likely to interact with Botox than others. Discuss your specific medication regimen with your doctor.
Botox Dosing Adjustments: In some cases, your doctor may need to adjust the dosage of Botox based on your individual response to the medication or any pre-existing medical conditions.
Post-Treatment Monitoring: After undergoing Botox treatment while on medications, monitor yourself for potential side effects and report them to your doctor if they occur.
Special Precautions: Pregnant women, nursing mothers, individuals with autoimmune disorders (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis), and those with a history of botulism or neurological conditions may require special precautions when undergoing Botox treatment.
Lifestyle Considerations: Certain lifestyle factors, such as smoking and excessive sun exposure, can increase the risk of side effects or reduce the effectiveness of Botox. Discuss your individual circumstances with your doctor to determine the best course of action.
Certain medications can interact with botulinum toxin, such as Botox, increasing the risk of side effects.
This interaction is due to the fact that some medications affect how the body breaks down and uses the toxin, leading to an accumulation of its active ingredients in the body.
For example, medications that inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase can increase the levels of botulinum toxin in the body, which can lead to increased muscle weakness or paralysis.
Another class of medications, called anticholinergics, also increase the risk of side effects when combined with Botox.
Anticholinergic medications work by blocking the action of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that helps regulate muscle contractions and other bodily functions.
When taken with Botox, these medications can amplify the effect of the toxin, leading to an increased risk of side effects such as drooping eyelids, facial weakness, or difficulty swallowing.
Corticosteroids, which are often used to treat inflammatory conditions, can also interact with Botox and increase the risk of side effects.
Other medications that may interact with Botox include blood thinners, beta-blockers, and certain antidepressants.
It’s essential for individuals considering Botox treatment while on medication to discuss their specific medications and medical history with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist.
This discussion will help identify potential interactions between the medication and the Botox, allowing for safe and effective treatment planning.
Additionally, patients should be aware of the signs and symptoms of side effects, which can include pain, redness, swelling, bruising, or difficulty swallowing at the injection site.
If any of these side effects occur, it’s crucial to contact a healthcare professional immediately for guidance and treatment.
Book a Consultation for Dermal Fillers with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
In some cases, alternative treatments may be available that do not involve botulinum toxin, such as fillers or other injectable medications.
Ultimately, the decision to undergo Botox treatment while on medication should be made in consultation with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist who can provide personalized guidance and care.
Botox treatment can be used by individuals taking various medications, but it’s crucial to consider some general factors before undergoing treatment.
- Medications that affect the nervous system or muscles may interact with Botox. For example, certain antidepressants, antipsychotics, and muscle relaxants can affect how Botox works or increase the risk of side effects.
- Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, can thin the skin, making it more susceptible to bruising during Botox treatment. This may require additional precautions or a longer recovery time.
- Sedatives and tranquilizers can increase the risk of dry mouth, which may lead to increased salivation during Botox treatment. This could potentially cause unwanted effects such as blurred vision or drooping eyelids.
It’s essential for individuals taking medications to consult their doctor before undergoing Botox treatment. A thorough medical evaluation will help determine whether Botox is safe and effective for each patient.
Clinical studies have investigated the interactions between various medications and Botox:
- Studies have shown that medications like antidepressants, antipsychotics, and muscle relaxants do not significantly affect the efficacy of Botox. However, they may increase the risk of side effects.
- A study on corticosteroids found that prednisone did not alter the onset or duration of Botox effects. Nevertheless, patients taking high doses of corticosteroids required additional precautions to minimize skin bruising and swelling during treatment.
- Research has demonstrated that sedatives and tranquilizers do not significantly impact Botox treatment outcomes. Nonetheless, they may increase the risk of dry mouth, which could lead to unwanted side effects.
Get Started with Dermal Fillers – Book with Dr. Laura Geige
Professional guidelines for using Botox while on medication vary depending on the medical context:
- The American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) emphasizes the need for a comprehensive pre-treatment evaluation to ensure patient safety. They recommend considering interactions between medications and Botox before proceeding with treatment.
- The American Academy of Dermatology suggests that patients taking certain medications, such as corticosteroids and sedatives, may require additional precautions or monitoring during Botox treatment.
It’s crucial for healthcare professionals to carefully assess the individual patient’s medical history, including medication use, before administering Botox. This ensures that patients receive safe and effective treatment, taking into account potential interactions between their medications and Botox.
Botox, a neurotoxin protein, has been widely used for various cosmetic and therapeutic purposes, including the treatment of facial wrinkles and spasms. However, its use in patients taking certain medications or with specific medical histories requires careful consideration due to potential interactions.
The American Academy of OtolaryngologyHead and Neck Surgery Foundation (AAOHNSF) has issued guidelines cautioning against using Botox in patients who take medications that affect neuromuscular transmission or have a history of neuromuscular disorders. These precautions are essential to ensure the safe administration of Botox.
Medications that affect neuromuscular transmission include those used to treat conditions such as myasthenia gravis, Lambert-Eaton syndrome, and botulism. Patients taking these medications may be at increased risk of developing dysphagia, respiratory failure, or other serious complications when Botox is administered.
Furthermore, patients with a history of neuromuscular disorders, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) or spinal muscular atrophy, should exercise extreme caution when using Botox. These conditions affect the functioning of muscles and nerves, making it difficult to predict how Botox will interact with their underlying condition.
Moreover, Botox can also be contraindicated in patients who have experienced adverse reactions to neuromuscular blocking agents or anesthetics. In such cases, the risks associated with Botox administration may outweigh its benefits.
A comprehensive medical history and thorough evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional are crucial before administering Botox to patients taking medications that affect neuromuscular transmission or with a history of neuromuscular disorders.
During this evaluation, the patient’s medication regimen, medical history, and any underlying conditions must be thoroughly assessed. The healthcare provider should also consider factors such as the duration of treatment with Botox, the dose administered, and the specific indications for use.
If a potential contraindication is identified, alternative treatments can be explored, and the patient’s risks and benefits should be carefully weighed. In some cases, discontinuing medications that affect neuromuscular transmission may be necessary before proceeding with Botox treatment.
It is also essential to note that patients who have received Botox in the past should not receive it again without consulting their healthcare provider first. This ensures that any potential risks or interactions are properly assessed and managed.
In conclusion, while Botox can be a highly effective treatment for various conditions, its use requires careful consideration of medications taking, neuromuscular disorders, and other medical factors. By exercising caution and conducting thorough evaluations, healthcare providers can minimize the risk of adverse reactions and ensure safe administration of Botox.
Medications to Approach with Caution
Medications can significantly impact the efficacy and safety of various treatments, including *_Botox_* injections. It is essential for individuals taking certain medications to understand which drugs may interact with *Botox* or other injectables, allowing them to make informed decisions about their treatment plans.
**Anticholinesterases** are a class of medications that can increase the risk of *_myasthenia gravis_*, a condition characterized by muscle weakness and fatigue. Individuals taking anticholinesterase medications should exercise caution when receiving *Botox* injections, as this combination may exacerbate the condition.
Some common anticholinesterases include *_pyridostigmine_* (Mestinon), *_neostigmine_* (Prostigmin), and *_amifryltoxin_* (Exalgo). If you are taking any of these medications, it is crucial to discuss your treatment options with a qualified healthcare professional before scheduling *Botox* appointments.
**Neuromuscular blockers**, such as *_succinylcholine_* and *_vecuronium_*, can also interact with *Botox*. These medications work by temporarily paralyzing muscles, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions when combined with *Botox* injections.
Individuals taking neuromuscular blockers should carefully weigh the risks and benefits of receiving *Botox* treatments while on these medications. It is also vital to inform a healthcare professional about all current and past medications, including over-the-counter supplements and vitamins.
A **healthy lifestyle** and regular exercise can help mitigate some side effects associated with *Botox*. However, individuals taking certain medications should prioritize caution when considering *Botox* injections. By understanding the potential interactions between medications and treatments, individuals can make more informed decisions about their health and beauty routines.
A healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance on using *Botox* safely while taking specific medications. They may recommend alternative treatments or adjust dosages to minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
Botox is a popular non-surgical treatment for various cosmetic and therapeutic concerns, but like any medication, it can interact with other substances in the body.
One potential interaction of concern is with anticholinesterase medications, such as neostigmine, which are commonly used to treat myasthenia gravis. Myasthenia gravis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that weakens muscle control, and anticholinesterase medications work by increasing the levels of acetylcholine in the body, a neurotransmitter involved in muscle contraction.
The study published in the Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neurology suggests that Botox may interact with neostigmine in individuals with myasthenia gravis. When anticholinesterase medications are taken concurrently with Botox, it can potentially enhance the effects of Botox, leading to an increased risk of side effects such as muscle weakness, fatigue, or respiratory problems.
Another medication that requires caution when using Botox is certain anticoagulants, such as warfarin. Warfarin is a blood thinner used to prevent and treat blood clots, but it can also increase the risk of bleeding when combined with Botox.
The interaction between Botox and anticoagulants is thought to be due to the way both medications work in the body. Botox relaxes facial muscles by blocking nerve impulses that cause muscle contractions, while warfarin works by inhibiting the production of vitamin K, a necessary factor for blood clotting.
A third medication that requires careful consideration when using Botox is beta-blockers. Beta-blockers are commonly prescribed to treat high blood pressure, heart conditions, and certain anxiety disorders. However, they can also mask symptoms such as tremors or palpitations, which may be beneficial in treating migraines with aura.
When taken concurrently with Botox, beta-blockers can reduce the effectiveness of Botox by blocking its action on nerve impulses. Additionally, beta-blockers can cause bradycardia (slow heart rate), a side effect that may worsen symptoms of conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Other medications that require caution when using Botox include sedatives and tranquilizers, which can increase the risk of excessive sedation, muscle relaxation, or respiratory depression when combined with Botox.
It is essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking before undergoing Botox treatment. This includes prescription medications, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and supplements. Your healthcare provider can help you weigh the benefits and risks of using Botox in conjunction with other medications and make an informed decision.
Ultimately, careful consideration and consultation with a qualified healthcare professional are crucial when determining whether it is safe to use Botox while on medication. By taking the necessary precautions, individuals can minimize the risk of adverse interactions and ensure a successful treatment outcome.
Medications such as antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications can interact with other substances, including botulinum toxin-based treatments like Botox.
Antidepressants, particularly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can affect the metabolism of certain drugs, including Botox. This may lead to increased levels of the drug in the body, increasing the risk of side effects such as bruising and bleeding at the injection site.
Anti-anxiety medications, like benzodiazepines, can also interact with Botox. The combination may increase the risk of excessive sedation, dizziness, or lightheadedness after treatment.
Botox is generally not a contraindication for people taking antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications; however, caution should be exercised when considering this treatment.
Before undergoing Botox injections, individuals taking these medications should discuss their treatment options with their healthcare provider. They may need to take additional steps to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
In some cases, stopping antidepressant or anti-anxiety medication use before getting Botox injections may be necessary. However, this decision should only be made under close medical supervision.
Closely monitoring for side effects and adjusting treatment plans accordingly is essential to ensure safe and effective outcomes.
Individuals taking medications like antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications should inform their healthcare provider about all medications, including over-the-counter and herbal supplements, before undergoing Botox treatment.
This information can help healthcare providers tailor their recommendations for safe and effective use of Botox while managing underlying medical conditions or taking medications.
Botox, a popular cosmetic treatment used to relax facial muscles and reduce wrinkles, may pose risks when combined with certain medications.
A review article published in the Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology highlights potential interactions between Botox and various classes of medications, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and other antidepressants.
SSRIs are commonly prescribed for anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), social anxiety disorder, and panic disorder.
When taken alongside Botox, SSRIs can increase the risk of muscle weakness, facial asymmetry, and eyelid drooping – all potential side effects of Botox treatment.
Avoiding concurrent use is recommended when starting Botox while on an SSRI or antidepressant medication to minimize these risks.
Another class of medications that may interact with Botox includes monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), tricyclic antidepressants, and atypical antipsychotics.
MAOIs are used to treat depression, anxiety disorders, and other conditions, but their interaction with Botox can lead to unpredictable effects such as abnormal muscle contractions or twitching.
Tricyclic antidepressants are also known for interacting with Botox, potentially causing adverse reactions like double vision, eyelid drooping, or facial weakness.
Atypical antipsychotics may interact with Botox by affecting the brain’s neurotransmitter systems, leading to unpredictable effects on muscle tone and movement.
Other medications that should be used cautiously when combined with Botox include beta-blockers, which are often prescribed for anxiety disorders or high blood pressure.
Beta-blockers can decrease the effectiveness of Botox by preventing it from reaching its target muscles, potentially reducing the treatment’s efficacy.
Anticholinergics and antihistamines should also be used with caution when combined with Botox, as they may exacerbate side effects like dry mouth, blurred vision, or constipation.
It is essential for individuals considering Botox to consult their healthcare provider about any medications they are currently taking before starting treatment.
A comprehensive evaluation of medical and medication history will help ensure safe and effective use of Botox.
This review article serves as a reminder for patients, providers, and researchers to carefully consider potential interactions between medications and Botox treatments to optimize outcomes and minimize risks.
Read more about The New Cinema Magazine here. Read more about Fashionably Balanced here. Read more about My Better Love here. Read more about Humboldt Apothecary CBD here. Read more about My Better Love here.
- Choosing The Best Nu-Derm Skin System Clinic In London - May 5, 2025
- Is Vista Edge Vape Worth It? A Deep Dive Into Its Pros & Cons - May 4, 2025
- Lip Flip Treatment Near Ottershaw, Surrey - May 4, 2025
